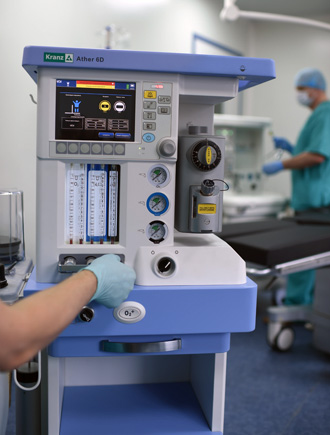
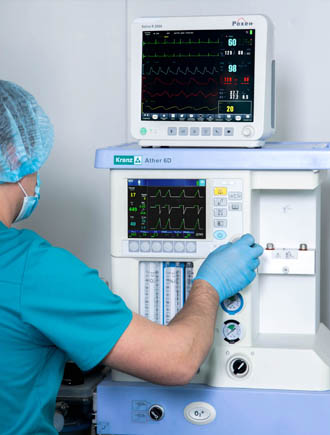
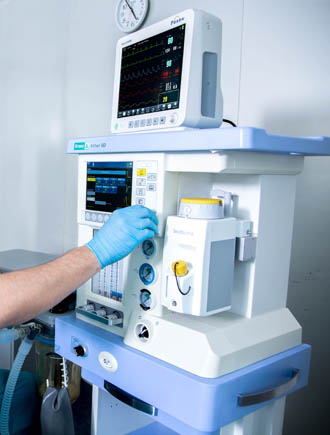
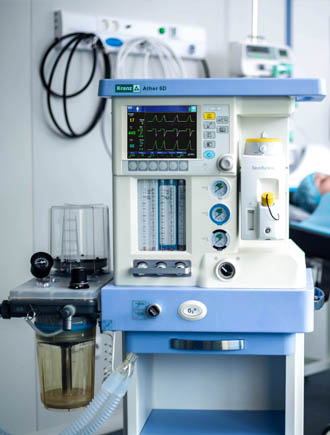
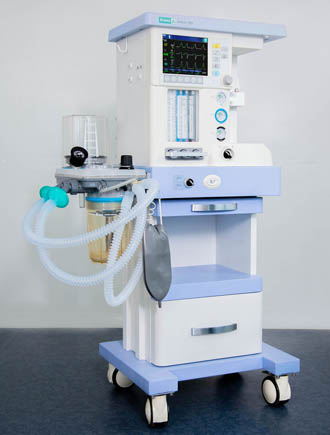
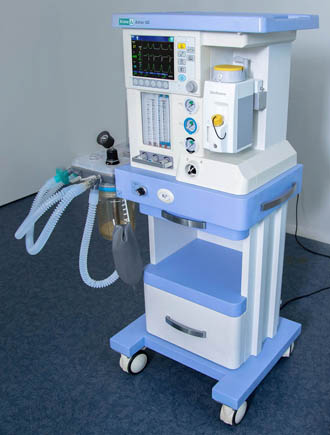
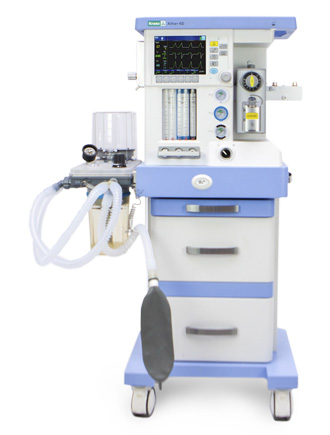
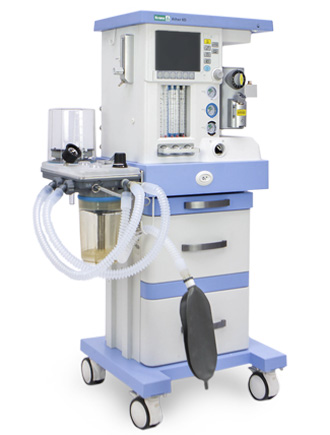
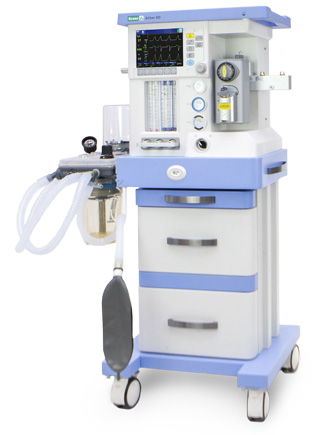
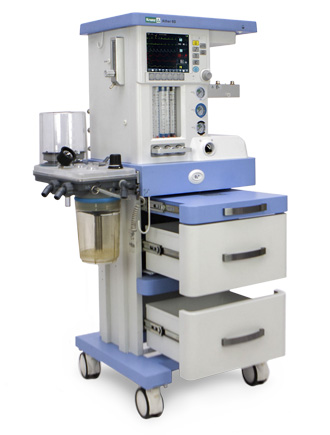
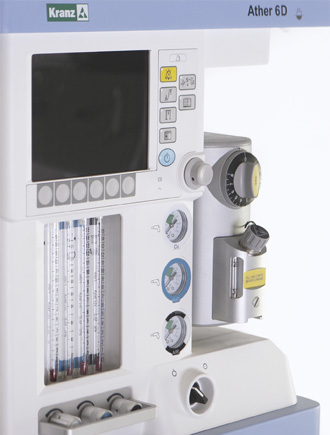
Anaesthetic and respiratory apparatus
Ather 6 D
Anesthesia machine is an automatic pneumatic device with electronic control which allows for a variety of respiratory support options. The device is designed for inhalation anesthesia, artificial ventilation during anesthesia for adult patients or children.
Anesthesia machine Ather 6D has the following features:
- total number of gases: 3
- mechanical flowmeter unit: two flowmeters for each gas
- protection against hypoxic mixture
- large LCD display
- using 2 vaporizers with the possibility of switching off each of the breathing circuit
- pneumatic drive
- monitoring of respiratory parameters
The Ather 6D anaesthetic and respiratory apparatus is designed for performing inhalation anesthesia in the operating room for adult patients and children with a body weight over 5 kilograms. The device can operate with low and minimal gas flows.
It has a built-in display showing the parameters of ventilation, respiratory monitoring and basic settings. Its interface is configured using membrane keys and a manipulator. Ather 6D has a built-in automatic leak compensation system, an electronic PEEP valve and mechanical flowmeters. It can be mounted and also use two evaporators.
The device uses vaporizers of inhaled anesthetics that are compatible with the lockable «Selectatec» mount. It can work sequentially with two evaporators, using liquid inhalation agents: halothane, isoflurane, sevoflurane.
Working with the device can be made more convenient by using a built-in illumination of the working field.
The gas supply to the anesthesia and respiratory apparatus is carried out from high-pressure sources (centralized wiring or an autonomous source). The gas supply is important for ensuring the operation of the pneumatic actuator. Three gases are used for the operation of the device: oxygen, air and nitrous oxide.
Mechanical flowmeters are designed to regulate the amount of gas flow supplied to the patient. Each flowmeter is designed for a certain type of gas and has two tubes. The functioning of the oxygen and nitrous oxide flow control knobs is interconnected, which prevents the assignment of a hypoxic mixture to a patient. An emergency oxygen supply button is provided.
The respiratory system module consists of the following units: a respiratory system itself, a carbon dioxide absorber, a membrane box, a pressure gauge that controls the pressure in the respiratory tract. Switching the device to the «spontaneous breathing/manual ventilation» and «automatic ventilation» modes is carried out using a special switch. The pressure level in the patient's airways in the mode of spontaneous and manual ventilation can be adjusted via the APL valve.
The anaesthetic ventilator is operated by an electronically controlled pneumatic actuator, which allows the use of various lung ventilation modes. In particular, the following modes are available: the volume-controlled mode (VCV), the pressure-controlled mode (PCV), intermittent forced ventilation with volume control (vSIMV), intermittent forced ventilation with pressure control (pSIMV), pressure support (PSV), optional spontaneous breathing (SPONT) and pressure-controlled ventilation with volume control (PRVC). All mode settings can be seen on the display, which also provides the representation of graphical parameters of a particular ventilation method in real time.
When the anesthesia device is turned on, the start screen appears, where you can select the patient's category (adult or child), set his weight, select the ventilator mode, start the operating mode or reset all the default settings.
The main screen appears when the operating mode is started. You can see the set and measured parameter values on it.
The Ather 6D anaesthetic and respiratory apparatus is equipped with built-in rechargeable lithium batteries that ensure uninterrupted operation when the external power is turned off. The batteries are charged when connected to the AC network in the switched-on state. If there is no power from the mains, the device automatically switches to battery power, notifying the user about this.
Main characteristics
| Ventilation mode |
- Manual Ventilation - Spontaneous Ventilation - Volume Control Ventilation (VCV) - Pressure Control Ventilation (PCV) - Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation Volume Control with Pressure Support Ventilation (SIMV(V)+PS) - Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation Pressure Control with Pressure Support Ventilation (SIMV(P)+PS) - Pressure Regulated Volume Control (PRVC) - Apnea Ventilation Mode |
| Regulated parameters |
- Tidal Volume (VT) - Inspiratory Pressure (Pinsp) - Pressure Limit (Plimit) - Breath Rate (Frequency) (f) - TI : TE - Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) - Inspiratory Pause - Time Of Inspiration TI - FTRIG - PSUPP |
| Monitored parameters |
- Tidal Volume - Minute Volume - Breath Rate (Frequency) - Airway Pressure - FiO2 |
| Power supply |
- AC power - internal rechargeable battery |
| Option |
- integrated aspirator - drawers (up to 3 pieces) - extendable work surface |
General characteristics
| The anesthetic machine is designed for inhalation anesthesia for adults and children weighing more than 5 kg. | |
| Groups of Patients: | children (weigh: 5 ~20 kg) adults (weigh: 20 ~ 150 kg) |
| Gas supply specification: | Air Nitrous oxide Oxygen |
| pneumatic drive | |
| Monitoring the gas supply pressure with pressure gauges for each gas | |
| Types of inhalation anesthesia: semi-open-circuit anesthesia, semi-closed-circuit anesthesia, closed-circuit anesthesia | |
| Breathing system volume, including the absorber, ml, no more | 2800 |
| Anaesthetic gas scavenging system | |
| External display, TFT | Display size (inches) — 8.0 Touch-screen function Control type: touch-screen, keys, navigation wheel |
| Gas supply requirements: | |
| connection with medical gas supply pipelines | |
| number of pipelines for the supply of medical gases, pcs., not less than | 3 |
| length of medical gas supply pipelines, m, not less than | 3 |
| Types of connected medical gases: Oxygen, Nitrous oxide, Air | |
| Mechanical flowmeter for each gas (Oxygen, Air, Nitrous oxide) | |
| Gas mixture flow control range, L/min: | Oxygen: 1–15 Nitrous oxide: 1–15 Air: 1–15 |
| Permissible pressure range of connected medical gases (dry and clean), MPa | 0,28 ~ 0,60 |
| indication of the gas mixture flow rate for each of the gases: oxygen, nitrous oxide, air | |
| oxygen concentration in the fresh breathing mixture,%, in range; | 21 - 100 |
| blocking the supply of nitrous oxide when the oxygen supply is stopped | |
| overpressure relief valve | |
| emergency oxygen supply | |
| O2 flush flow, L/min | 25 ~ 75 |
| Driving gas with priority for air, oxygen additionally | |
| Respiration system requirements: | |
| Auxiliary common gas outlet(ACGO) | |
| heating function of the the patient absorber system | |
| safety valve that allows the patient to breathe the air of the room in case of a malfunction of the device | |
| Carbon dioxide absorber requirements: | |
| reusable carbon dioxide absorber canister with capacity, ml, not less; | 1500 |
| bypass function of the absorber | |
| Anesthetic agent vaporizer requirements | |
| One-station vaporizer mounting systems with interlock function | |
| Two-station vaporizer mounting systems with interlock function (option) | |
| Flow type of vaporizer of inhaled anesthetic | |
| Sevoflurane | |
| Isoflurane (option) | |
| Enflurane (option) | |
| Ventilation modes: | |
| Manual Ventilation | |
| Spontaneous Ventilation | |
| Volume Control Ventilation (VCV) | |
| Pressure Control Ventilation (PCV) | |
| Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation Volume Control with Pressure Support Ventilation (SIMV(V)+PS) | |
| Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation Pressure Control with Pressure Support Ventilation (SIMV(P)+PS) | |
| Pressure Regulated Volume Control (PRVC) | |
| Apnea Ventilation Mode | |
| Regulated characteristics: | |
| Oxygen concentration range | 21~100% |
| Tidal volume | 20~1500 ml |
| Respiratory rate | 4~100 min–1 |
| Inspiratory time | 0,1~10,0 sec |
| Inspiration pause | OFF, 5%~50% |
| Positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) range | 4~20 cmH2O |
| Pressure control range | 5~70 cmH2O |
| Pressure support range | 5~60 cmH2O |
| Flow trigger sensitivity | 1,0~15,0 l/min |
| Requirements for monitored and displayed parameters: | |
| tidal volume | |
| Minute ventilation | |
| Inspiratory oxygen concentration | |
| Airway pressure | |
| Inspiration platform pressure | |
| Airway peek pressure | |
| The average airway pressure | |
| PEEP | |
| Breathing frequency | |
| Inspiratory tidal volume | 0~2500 mL |
| Expiratory tidal volume | 0~2500 mL |
| Minute ventilation | 0~60 L |
| Inspiratory oxygen concentration | 21%~100% |
| Airway peek pressure | 0~100 cmH2O |
| Inspiration platform pressure | 0~100cmH2O |
| The average airway pressure | 0~100cmH2O |
| PEEP | 0~70cmH2O |
| Breathing frequency | 0~100bpm |
| Airway resistance | 0~200cmH2O/(L/S) |
| Compliance | 0~200mL/cmH2O |
| Requirements for graphical monitoring: | |
| Pressure-time, Flow-time, Volume-time, | |
| loops: volume-pressure, flow-volume, flow-pressure | |
| Notification requirements for medical personnel (alarm parameters) | |
| Audible alarm signals | |
| Light indicator alarm signals | |
| Function of temporary deactivation of alarm signal | |
| Settings of alarm signal limits | |
| High inspiratory oxygen concentration | |
| Low inspiratory oxygen concentration | |
| High gas supply pressure | |
| Low gas supply pressure | |
| High Tidal Volume | |
| Low Tidal Volume | |
| High minute ventilation | |
| Low minute ventilation | |
| High respiratory rate | |
| Low respiratory rate | |
| High airway pressure | |
| Low airway pressure | |
| Continuous high airway pressure | |
| Negative pressure alarm | |
| Low battery power | |
| Exhausted battery power | |
| AC power failure | |
| Battery failure | |
| O2 sensor disconnection or failure | |
| Absorber is not installed | |
| O2 flush overtime | |
| No gas in bellow | |
| Set value of flowmeter is too big | |
| Inspiration valve error | |
| Expiration valve error | |
| Inspiration pressure sensor failure | |
| E-xpiration pressure sensor failure | |
| 5V power error | |
| 10V power error | |
| 12V power error | |
| -12V power error | |
| Upper-limit alarm of the airway pressure | 1~100cmH2O |
| Lower-limit alarm of the airway pressure | 0~99cmH2O |
| Upper-limit alarm of the oxygen concentration | 21~100%, OFF |
| Lower-limit alarm of the oxygen concentration | OFF, 21~99% |
| Upper-limit alarm of the tidal volume | 20~1500mL,OFF |
| Lower-limit alarm of the tidal volume | OFF, 10~1500mL |
| Upper-limit alarm of the minute ventilation | 1~40L, OFF |
| Lower-limit alarm of the minute ventilation | OFF, 0~40L |
| Upper-limit alarm of the breathing frequency | 1~100 bpm |
| Lower-limit alarm of the breathing frequency | 0~99bpm |
| Upper-limit alarm of the end-expiratory CO2 (optional) | 1~100mmHg |
| Lower-limit alarm of the end-expiratory CO2 (optional) | 0~99mmHg |
| Suffocation alarm | 10~40s |
| Dimensions: | |
| height, mm, not more than | 1600 |
| width, mm, not more than | 845 |
| length, mm, no more than | 730 |
| Net weight, kg, not more than | 85 |
| Power supply: | |
| supply voltage | 100 ~ 240 V |
| frequency | 50/60 Hz ±1% |
| аutonomous battery power supply | |
| voltage | 11,1 V |
| capacity | 7800 mAh |
| provides operation in standard conditions not less than | 60 minutes |
| Operating environments: | |
| Temperature | +10℃ ~ +40℃ |
| Humidity | ≤80%, non-condensation |
| Atmospheric pressure | 70 kPa ~ 106 kPa |
| CO2 Module | option |
| Mainstream mode | option |
| Measurement range and accuracy, % (vol.) | 0–25 |
| MultiGAS module | option |
| Mainstream mode | option |
| CO2 measuring range (%) | 0–25 |
| N2O measuring range (%) | 0–100 |
| HAL, ENF, ISO measuring range (%) | 0–25 |
| SEV measuring range (%) | 0–25 |
| DES measuring range (%) | 0–25 |
Air Compressor
| Oil-free | |
| The rated output pressure range kPа (MPa) | 350 ~ 400 (0,35 ~ 0,4) |